Understanding Your Dog’s Behaviour: Tips on Interpretation and Effective Responses!

Their cute nature seems to give them that special place as a man’s best friend. So, how well do we really know our pets? Dogs are in constant state of toddlerhood; be they young or old, always curious, raucous, and downright bad. A dog’s behavior can be cute, funny, sad, weird, gross, and occasionally melt your heart with “Aww…” or frighten the life out of you which is a nightmare. But what does each behavior signify? And what do you need to do?
-
- Jumpy/Standing on Hind Legs
- Whining
- Barking
- Aggressive/Growling
- Howling
- Nipping/Play Biting
- Chasing/ Running
- Pulling Leash
- Chewing
- Bringing their toy
- Guarding Food
Jumpy/Standing on Hind Legs

Based on whether they are greeting human beings, excitedness, or attention-seeking, dogs may jump up or stand on their hind legs; however, jumping behavior may imply fear or aggression. It is critical to know the history of behavior to identify its underlying reason and design a fitting solution.
There are some steps to take:
- Ignore the Behavior: Don’t reward jumping by giving attention, as this can reinforce it.
- Redirect: Use commands like “sit” or “down” to focus their energy on calm behaviour.
- Positive Reinforcement: Give affection or treats to calm behavior.
- Consistency: Discourage jumping and reinforce desired behavior consistently.
- Training: Practice obedience training regularly to help your dog understand acceptable behaviour.
- Socialization: Well-socialized dogs usually do not jump because of fear.
Research from Frontiers in Veterinary Science analyzed both positive and aversive training methods and further explained how positive reinforcement benefits the obedience of canines and at the same time reduces stress levels.
Whining

One of the different types of vocal communication in dogs is whining. Dogs most often will whine when they want attention, excitement, anxiousness, or a sign of appeasement.
There are some steps to take:
- Evaluate the Situation: look for basic needs such as hunger, thirst, or dirty bathroom.
- Watch for Signs of Pain or Sickness: If the whining is relentless and seems strange, take them to the vet.
- Offer Comfort: If they are feeling anxious, comfort them with soothing voices or toys or other distractions.
- Prevent Reinforcing Bad Habits: Do not pet until they calm down; refrain from encouraging whining to be let alone.
Barking
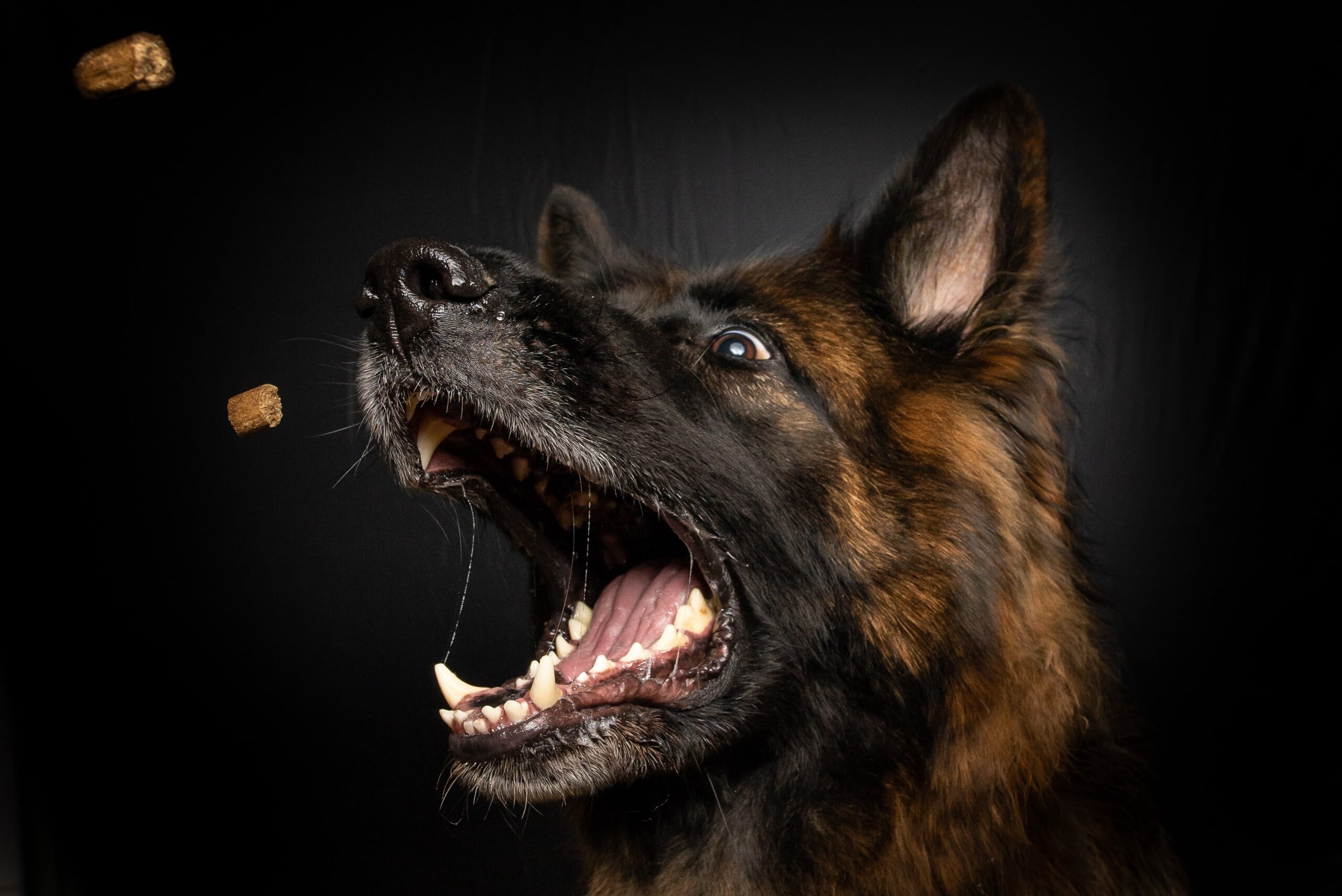

A dog bark can express widely different emotions, including warning, fear, or anxiety, depending on the context. Staccato cries may signal distress, accompanied by sharp barks of friendship or playfulness in between. Excessive barking is symptomatic of something wrong, either with the dog or with something else affecting those around her.
There are some steps to take:
- Identify Triggers: Pay attention to the situations and reasons behind your dog’s barking.
- Train Commands: Teach cues like “quiet” or “stop.”
- Stay Consistent: Reward good behaviour and avoid reinforcing excessive barking.
- Professional Assistance: See a behaviorist or dog trainer if the barking continues.
For scientifically-backed insights, check this detailed analysis: Read the study.
Aggressive/ Growling
Dog growling is a form of communication, often due to fear, territoriality, pain, or possession aggression. When dogs are unable to verbally communicate themselves, it indicates distress. Most dog aggression stems from fear or anxiety rather than the intent to harm, with other factors like socialization and guarding influencing behaviour.
There are some steps to take:
To handle dog aggression and growling:
- Stay Calm: Avoid reacting aggressively.
- Give Space: Let your dog retreat if needed.
- Identify Triggers: Observe what causes the behavior.
- Use Training: Reward calmness and redirect with commands.
- Avoid Punishment: Don’t suppress growling as it’s a warning.
- Rule Out Health Issues: Consult a vet to check for pain or illness.
- Consult a Professional: Seek help from a pet trainer or dog behaviour training for persistent aggression.
Here is the research on the effects of positive and aversive training methods, showing how positive reinforcement improves canine obedience and reduces stress: Research Outreach
Howling
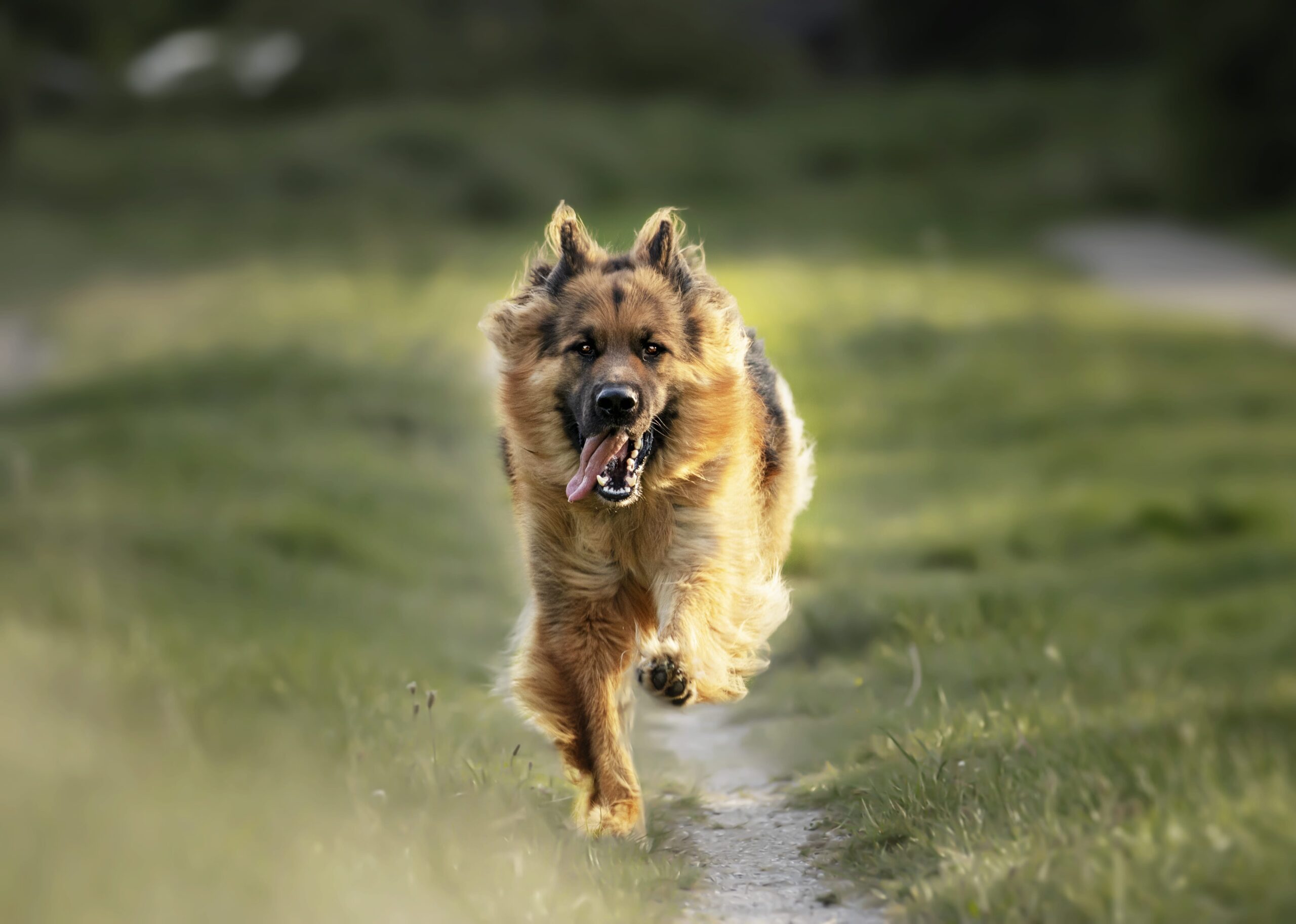

Howling is one of the ways dogs communicate vocally. They howl in order to get attention, bond with people, and express themselves. Some dogs may also scream due to the sound of high pitched sounds, such as ambulance sirens or specific musical instruments.
There are some steps to take:
- Find out the Cause: Howling could be due to loneliness, anxiety, boredom, or in response to things such as sirens or the howling of other dogs.
- Give Attention: Your Dog may be howling out for attention, and they’re probably under kinetic and mental stimulation.
- Use Distractions: Offer toys or engage in interactive play to redirect their focus.
- Address Anxiety: If howling is due to separation anxiety, try gradually increasing alone time or using calming products (like anxiety wraps).
- Exercise: Give your dog an ample amount of exercise to prevent any frustration.
- Consult a Vet: Talk to a vet if the howling happens often or with acute pain because that would need to rule out medical issues.
Nipping/ play biting

There are many reasons why dogs play-bite or nip, such as play, teething, attention, and exploration. Besides being a possible way of interaction or communication, most young puppies nip as a form of play or teething to soothe their gums. Training and redirection are key to managing this behaviour.
There are some steps to take:
- Redirect: Nipping by your pup often indicates that it is time for play or the little teeth are coming up. Don’t just leave them at it. Instead, guide them away and give them a chew toy to direct the nipping elsewhere.
- Use Positive Reinforcement: Reward calm behaviour and appropriate play.
- Teach Bite Inhibition: Gently say “no” and stop play if the biting is too hard, then resume when calm.
- Consistency: Be consistent in stopping nipping and offering alternatives.
- These Are The Teething Toys: Puppies should be given proper teething toys that relieve them from discomfort.
- Socialisation: Socialise your dog with other dogs so it will learn the proper way to play.
- Training: Regular training helps establish clear boundaries for appropriate behaviour.
Chasing/ Running
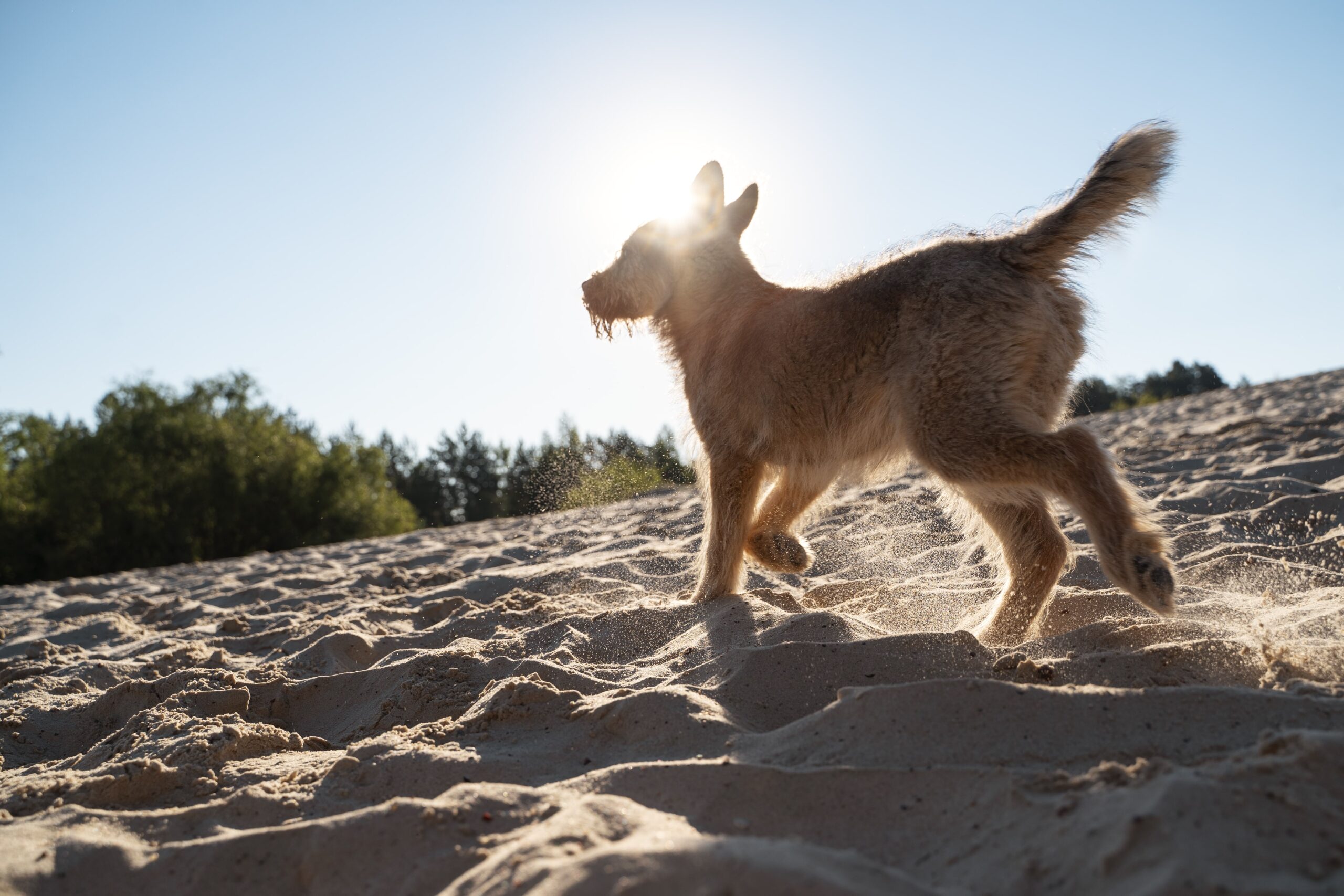

Dogs chase and run for several reasons, including playfulness, prey drive, curiosity, or release pent-up energy. Instinctively, they might chase people, other animals, or moving things. It’s often a fun and natural behaviour, but can also be a sign of excitement or a need for mental and physical stimulation.
There are some steps to take:
- Exercise: Provide exercise for your dog so it won’t be deprived of outside physical activities and mental stimulation such as walking, playing, and activities.
- Train the dog with Use Training: Commands such as “come,” “stay,” and “leave it” may also be a way to distract them from attention.
- Leashing and Harnessing: Use a leash for your dog in spaces where running would be a potential problem.
- Safe Play Areas: Make a fenced, safe space in which the dog can run freely of what captivates him.
- Mental Stimulation: Giving him puzzle toys and training exercises to keep his cerebral activities occupied.
- Change their focus: Use a toy or a command to refocus your dog’s attention if they begin chasing. Consider looking for local dog training or obedience classes in your area.
Pulling the leash
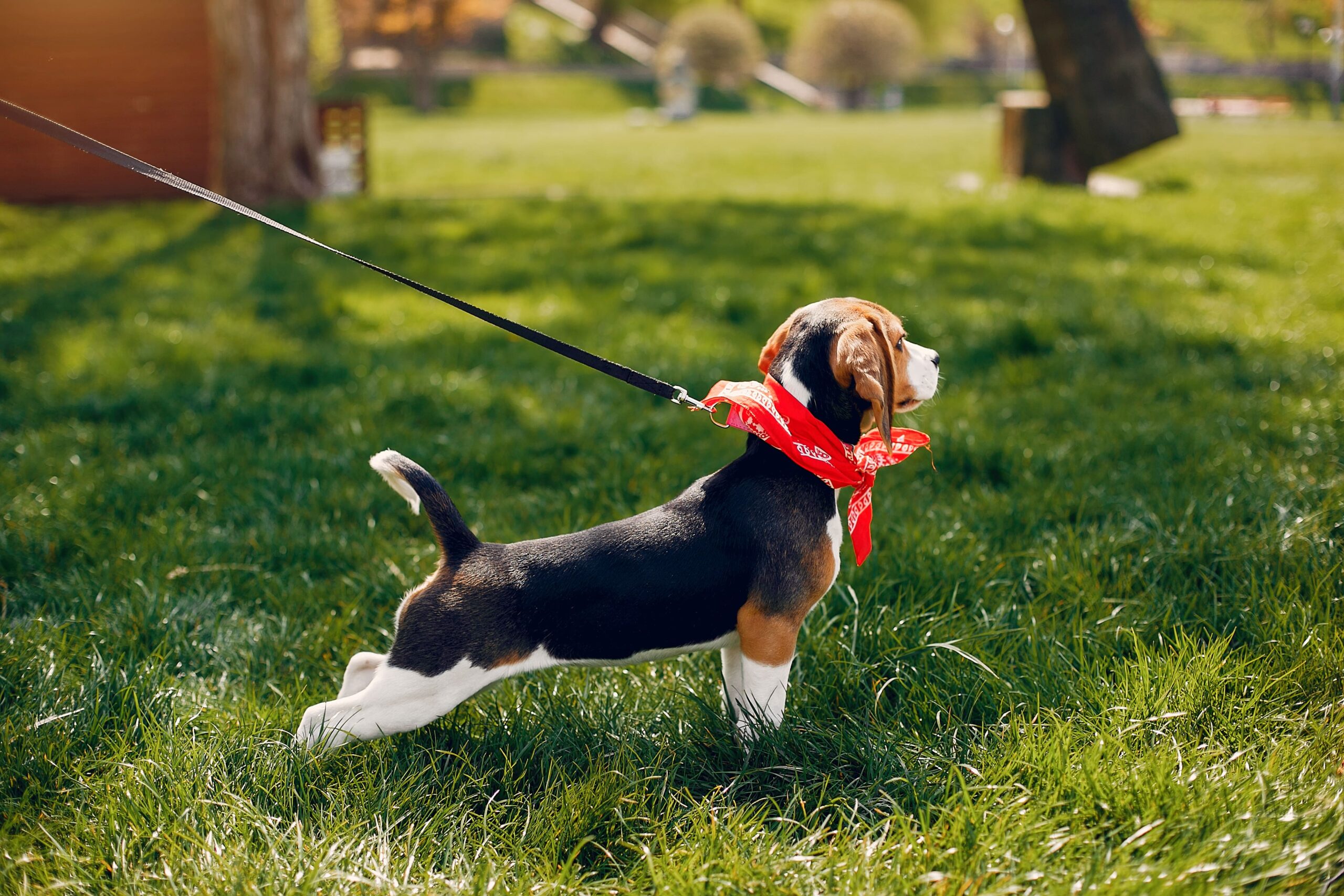

Dogs pull on the leash because they are interested in something like another dog, a smell, or a way to the park. Pulling and getting closer is a form of reinforcing the behaviour as it gets them closer. Since they’ve learned to tolerate tension, discomfort won’t stop them, making the problem escalate over time.
There are some steps to take:
- Using Positive Reinforcement: Train well your dog when your dog walks nicely with you.
- Pause Your Walk: When your dog pulls on the leash, stop walking immediately. Wait until the leash slackens and your dog settles down before continuing.
- Teach Loose Leash Walking: Practice walking with the leash loose, rewarding them for staying by your side, and exclusive training for not pulling on the leash while walking.
- Switch Directions: When your dog starts pulling, turn and walk the other way to encourage them to follow you.
- Harness with Front Clip: A harness with a front clip can help take the dog back toward you and stop the pulling.
- Consistency: Be consistent with training and avoid letting your dog pull for reward. Search for local dog training or obedience classes in your area.
Chewing
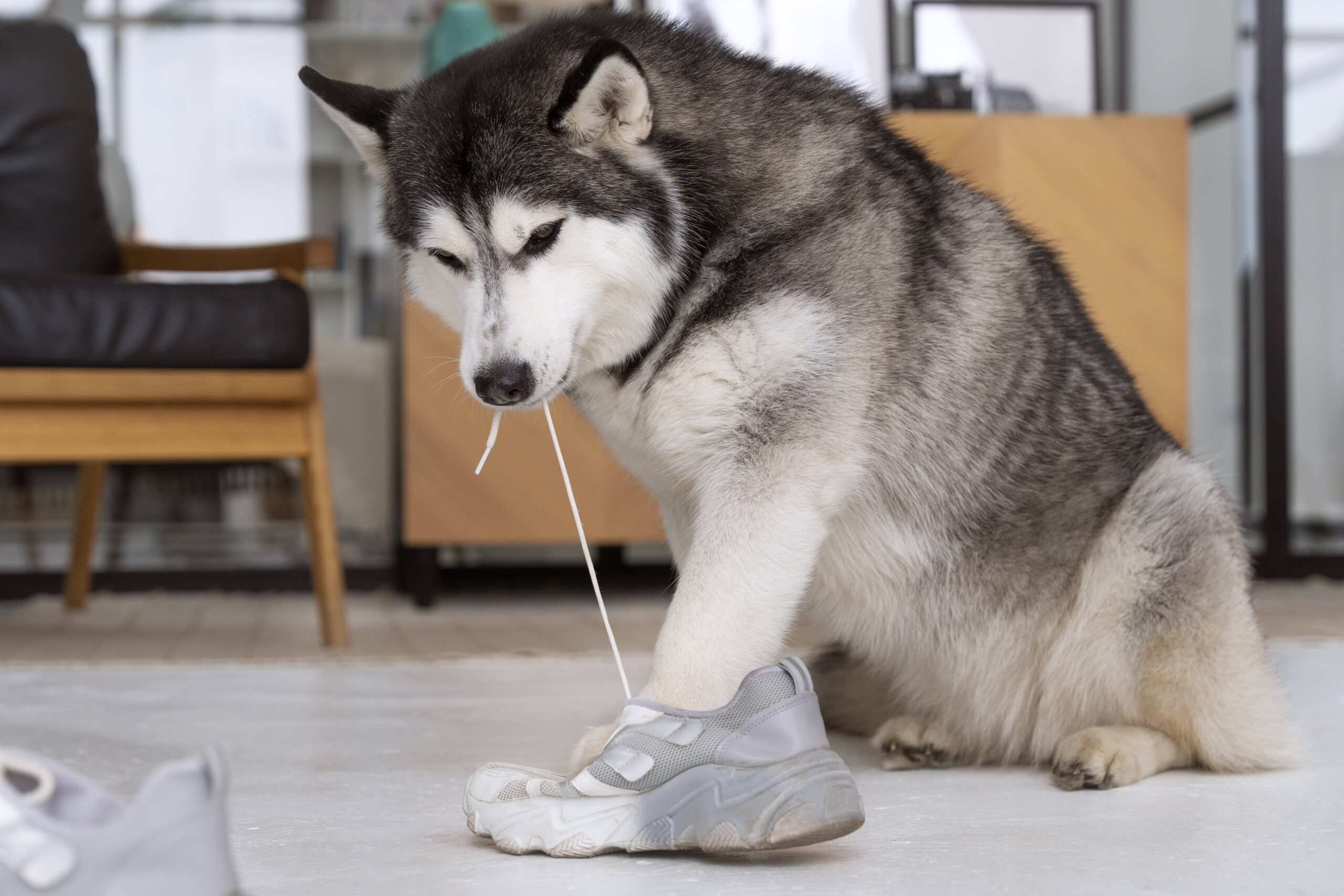

Dogs nibble to allow their teeth to come through, and sometimes they chew objects that may either bore or stimulate them. Anxiety and stress can also be responsible for such behavior. Chewing in dogs is a natural instinct that helps them explore their surroundings or find solace. Other times, they chew simply out of boredom; some take a chew because they’re seeking attention; and some are not mentally or physically stimulated enough.
There are some steps to take:
- Offer an Appropriate Toy: Provide Traditional Chew Toys to Deter Chewing Behavior.
- Gentle steering towards a toy is advised if the chewing object is inappropriate.
- Apply a bitter non-toxic spray to deter chewing on shoes or furniture. Behaviours such as “leave it” can be taught to stop undesired chewing.
- Eliminate Anxiety: Time relaxing practice or reduce fears if chewing is due to anxiety.
Bringing their toy

In more complicated situations, get advice from a certified behaviorist or trainer. It may also be a way for them to initiate a game or show affection. Some dogs bring toys as part of their instinct to share or engage in a bonding activity.
There are some steps to take:
- Play and Reward: Engage in play when your dog brings a toy, reinforcing positive interaction.
- Promote Independence: Provide toys and give them praise when they play independently if you want children to play by themselves.
- Establish Boundaries: Calmly reroute them to play quietly or with a different toy if their behavior becomes out of control.
- Teach Commands: Use “drop it” or “leave it” if you don’t want them to bring toys at specific times.
Guarding Food
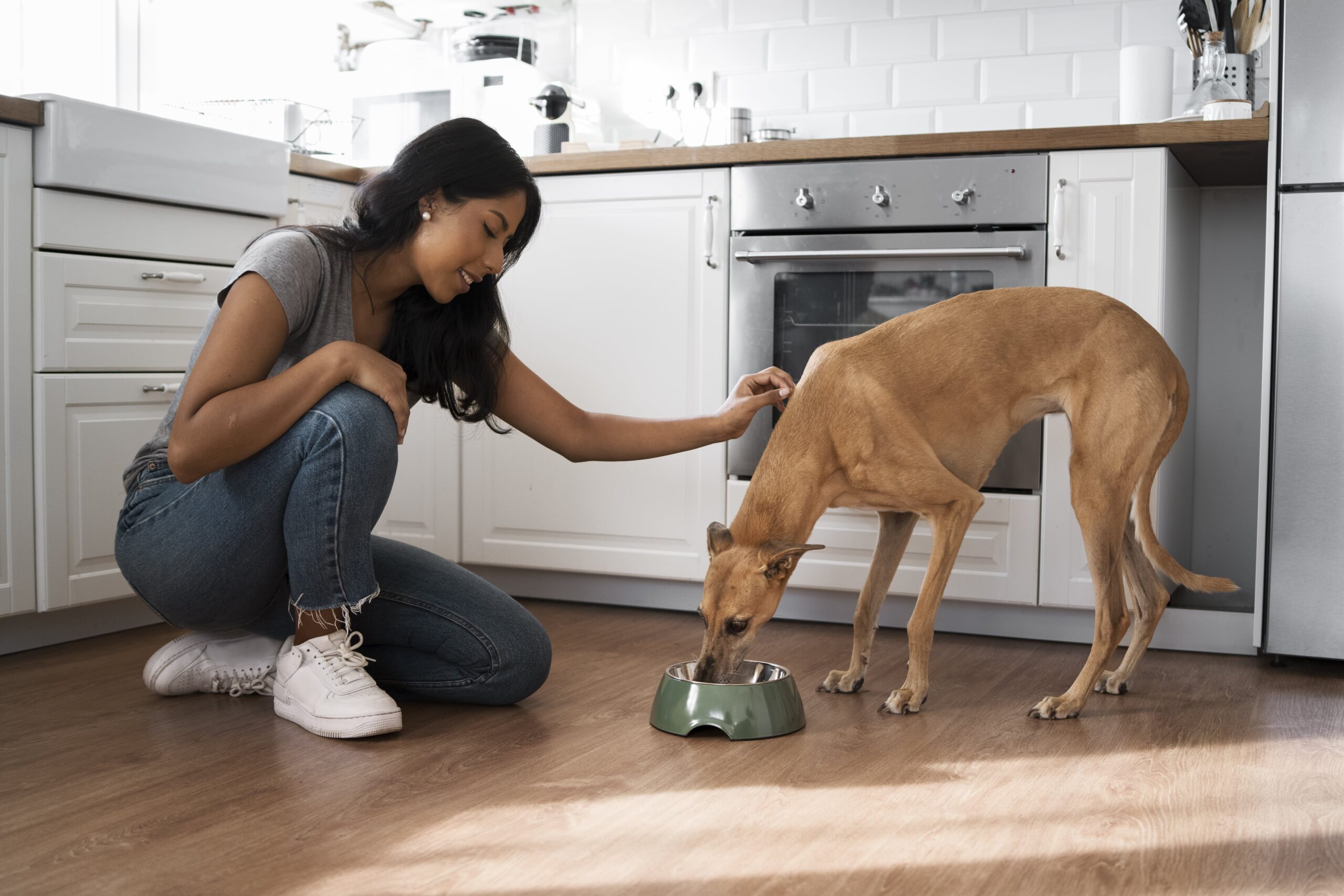

Dog food guarding includes resource guarding, which is the practice of protecting food toys or areas from other imagined dangers. This behaviour usually originates from feelings of fear, insecurity, and past experiences of scarcity. It can be an instinct, but it can lead to aggression if not managed properly.
What You Need to Do:
- Avoid Punishment: As it can exacerbate the behavior, never punish your dog for guarding.
- Desensitize Gradually: Gradually approach your dog while they are eating, reward them with treats, and assist them in creating positive associations with you.
- Hand Feeding: In order to develop trust and reduce defensive behavior, feed your dog by hand at times. Look in your area for dog obedience classes or dog training services.
- Establish Boundaries: Teach your dog to go to their designated eating spot and calmly wait for meals.
- Seek Expert Help: In serious situations, reach out to a professional trainer or behaviorist for proper advice and support.
Here is research that demonstrates some dogs that guard their food can be adopted and guarding is seldom seen in the home: Preliminary Investigation of Food Guarding Behavior.
Conclusion
Know your pet and regulate their behaviour in order to establish a meaningful and strong relationship between you and your paw-pal. They may bark or chew or hoard food; it only takes training and attention to turn everything around. Patience, consistency, and reward-based training are the three keys to effectively managing your dog’s bad behaviour. All this will be good in the long run, as it will cause your pet to develop good habits through this process while also setting up ways of being pleased and assured with your pet.
If you want further guidance or professional pet care advice, Petsfolio has professional recommendations for dog care, training, and health tips that will keep your dog happy.
References:
Send us a Message
Enjoy this post?
Check out some more great articles and other content.
When you walk your dog, you are engaging in constant non-verbal communication through...
Read The ArticleDog grooming myths in India are still widely believed, and this affects how pet paren...
Read The ArticleWhen a dog stops eating, it is one of the worst things that can happen to any pet own...
Read The Article
 Download App
Download App Join
Join Support
Support